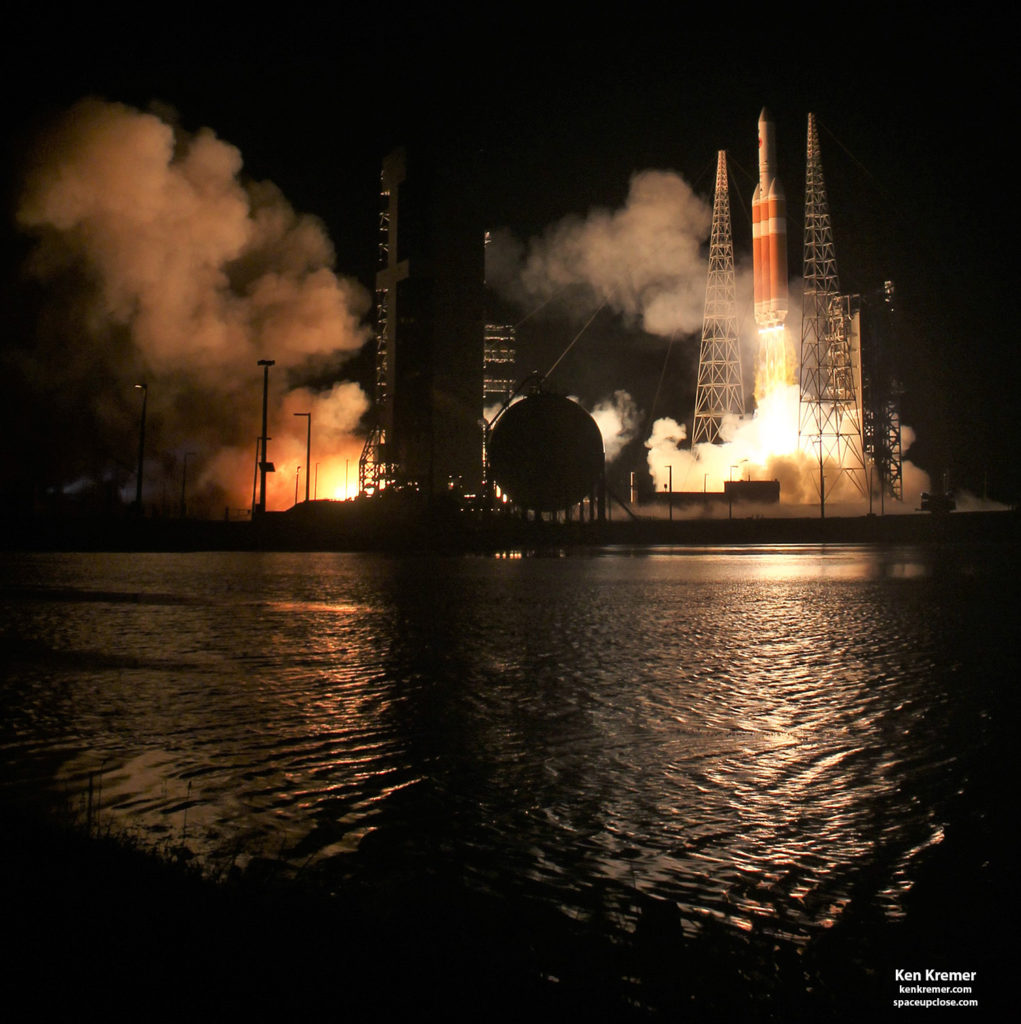
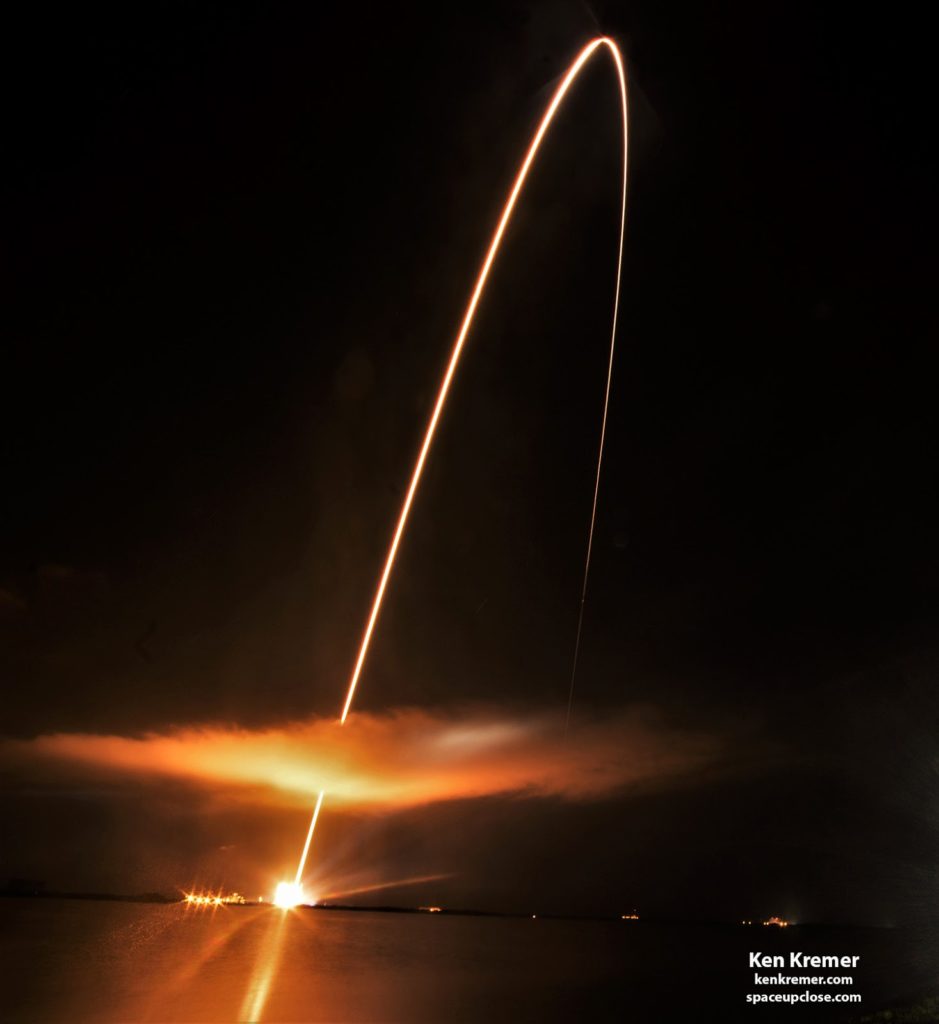
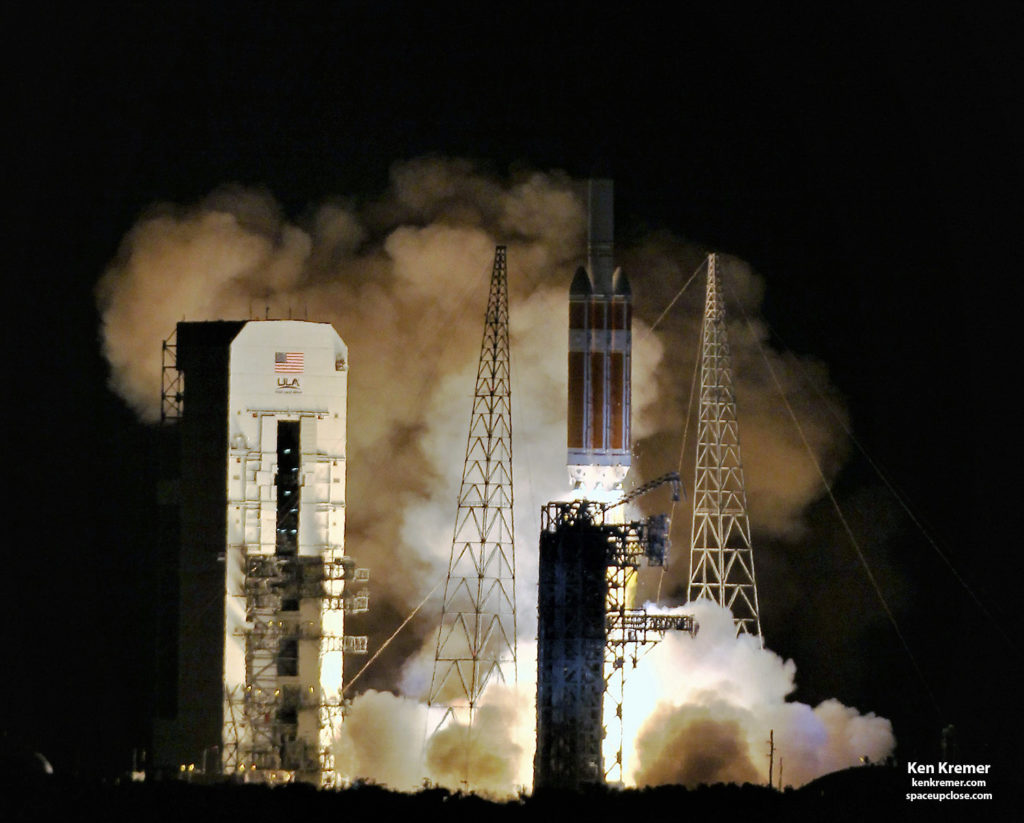
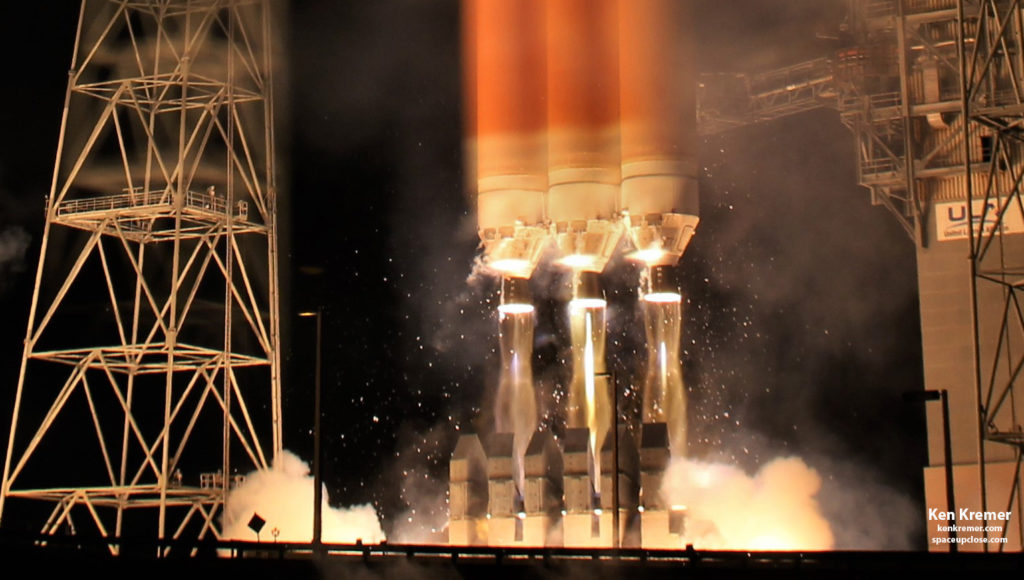
Ken Kremer — SpaceUpClose.com — 12 August 2018
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER,
FL – NASA’s Parker Solar
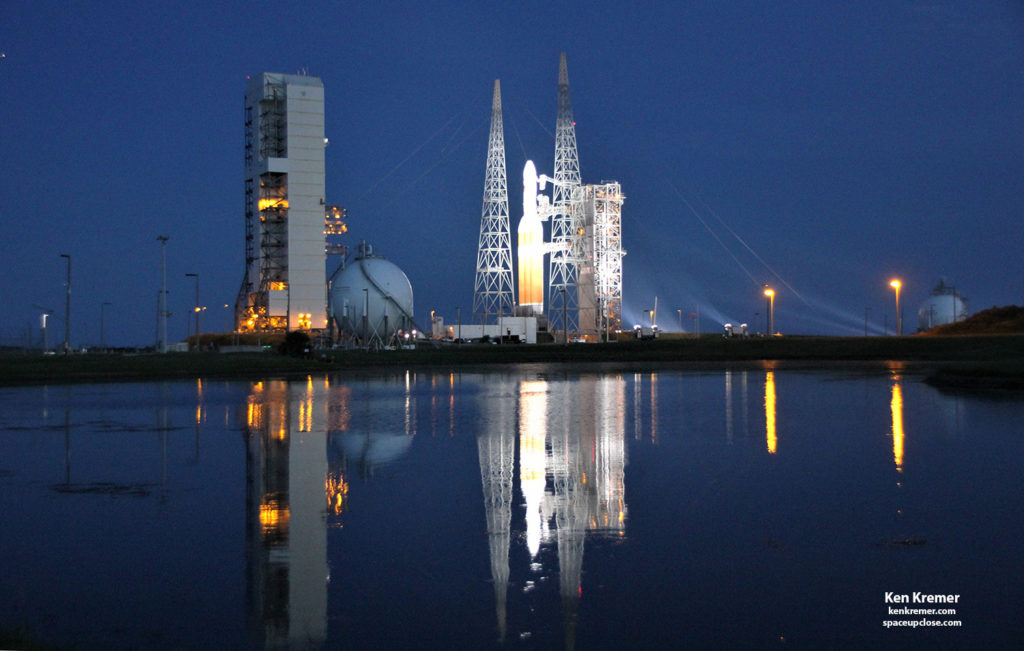
Probe spacecraft began its historic journey to touch the Sun with a magnificent
middle of the night launch early this morning from the Florida Space Coast atop
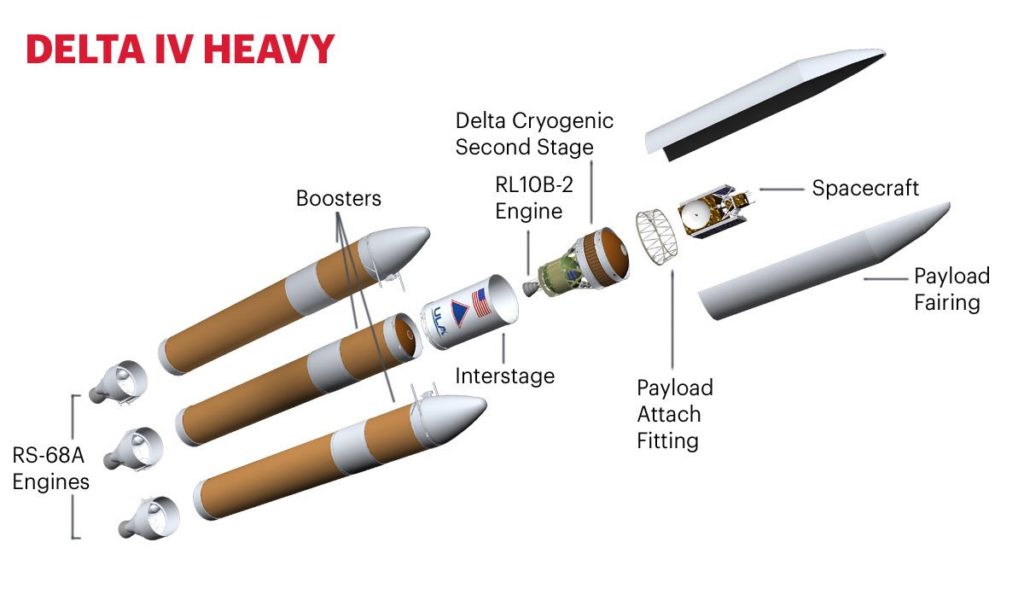
a powerful United Launch Alliance
Delta IV Heavy rocket.
Liftoff came a day late
for the $1.5 Billion car-sized Parker probe but no less splendid after resolving
a last moment technical glitch during the first launch attempt Saturday.
Weather was remarkably perfect
as the triple barreled beast came to life with a voluminous pool of yellow flame
raced up the side and orange exhaust flames billowed from the base as the trio
of RS-68 first stage engine ignited with over 2.1 million pounds of liftoff
thrust right at the opening of Sundays predawn launch window.
Here is the NASA Press release:
study, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe launched
from Florida Sunday to begin its journey to the Sun, where it will undertake a
landmark mission. The spacecraft will transmit its first science observations
in December, beginning a revolution in our understanding of the star that makes
life on Earth possible.
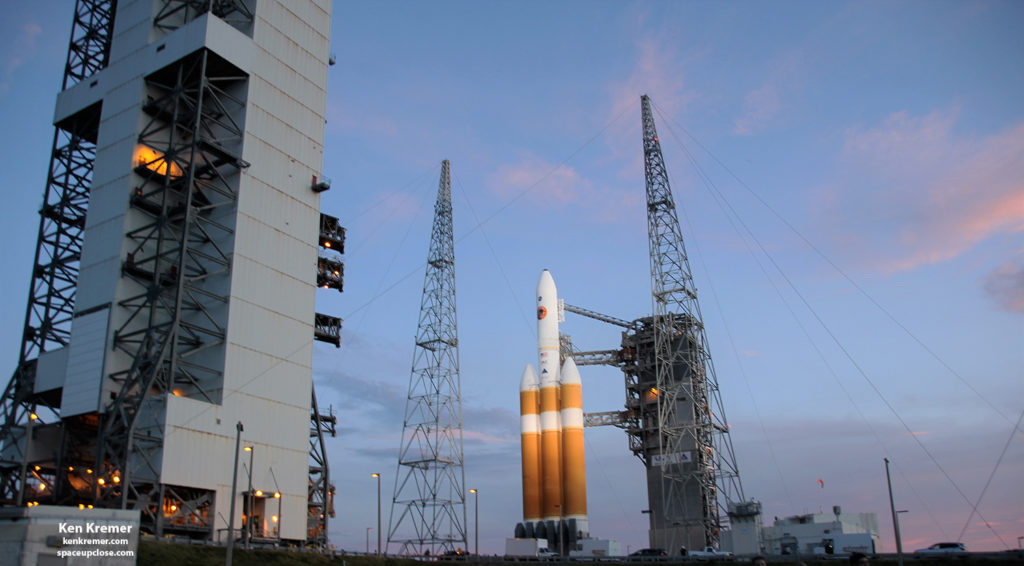
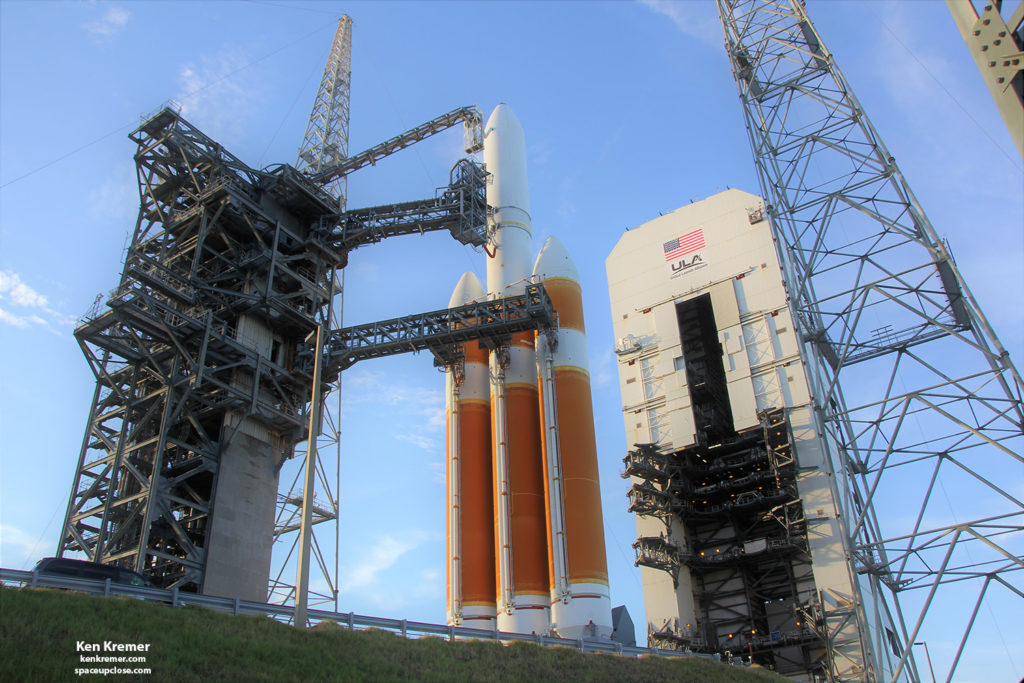
lifted off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket
from Space Launch Complex-37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. At 5:33 a.m.,
the mission operations manager reported that the spacecraft was healthy and
operating normally.
improve their forecasts of space weather events, which have the potential to
damage satellites and harm astronauts on orbit, disrupt radio communications
and, at their most severe, overwhelm power grids.
to a star that will have implications not just here on Earth, but how we better
understand our universe,” said Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator of
NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. “We’ve accomplished something that decades
ago, lived solely in the realm of science fiction.”
spacecraft will deploy its high-gain antenna and magnetometer
boom. It also will perform the first of a two-part deployment of its
electric field antennas. Instrument testing will begin in early September and
last approximately four weeks, after which Parker Solar Probe can begin science
operations.
decades of scientific study and millions of hours of effort,” said project
manager Andy Driesman, of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics
Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. “Now, Parker Solar Probe is operating
normally and on its way to begin a seven-year mission of extreme science.”
will fly towards Venus, performing its first Venus gravity assist in early
October – a maneuver a bit like a handbrake turn – that whips the spacecraft
around the planet, using Venus’s gravity to trim the spacecraft’s orbit tighter
around the Sun. This first flyby will place Parker Solar Probe in position in
early November to fly as close as 15 million miles from the Sun – within the
blazing solar atmosphere, known as the corona – closer than anything made by
humanity has ever gone before.
Probe will make six more Venus flybys and 24 total passes by the Sun,
journeying steadily closer to the Sun until it makes its closest approach at
3.8 million miles. At this point, the probe will be moving at roughly 430,000
miles per hour, setting the record for the fastest-moving object made by
humanity.
corona to solve long-standing, foundational mysteries of our Sun. What is the secret of the
scorching corona, which is more than 300 times hotter than the Sun’s
surface, thousands of miles below? What drives the supersonic
solar wind – the constant stream of solar material that blows
through the entire solar system? And finally, what accelerates solar energetic
particles, which can reach speeds up to more than half the speed of light as
they rocket away from the Sun?
than 60 years, but the investigation requires sending a probe right through the
unrelenting heat of the corona. Today, this is finally possible with
cutting-edge thermal
engineering advances that can protect the mission on its daring
journey.
has been one of the hardest challenges for space exploration,” said Nicola Fox,
project scientist at APL. “We’re finally going to be able to answer questions
about the corona and solar wind raised by Gene Parker in 1958 – using a
spacecraft that bears his name – and I can’t wait to find out what discoveries
we make. The science will be remarkable.”
suites designed to study magnetic fields, plasma and energetic particles, and
capture images of the solar wind. The University of California, Berkeley, U.S.
Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, University of Michigan in Ann Arbor,
and Princeton University in New Jersey lead these investigations.
a Star program to explore aspects of the Sun-Earth system that directly affect
life and society. The Living with a Star program is managed by the agency’s
Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for NASA’s Science Mission
Directorate in Washington. APL designed and built, and operates the spacecraft.
the physicist who first theorized the existence of the solar wind in 1958. It’s
the first NASA mission to be named for a living researcher.
 |
|
Credit: Ken
Kremer/kenkremer.com/spaceupclose.com |
attached to the spacecraft in May. It includes a quote from the renowned
physicist – “Let’s see what lies ahead.” It also holds a memory card containing
more than 1.1 million names submitted by the public to travel with the
spacecraft to the Sun.
Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Orbital ATK and more space and mission reports direct
from the Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida and
Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human
spaceflight news: www.kenkremer.com
–www.spaceupclose.com – twitter @ken_kremer – email: ken at kenkremer.com