Ken
Kremer — SpaceUpClose.com &
RocketSTEM – 24 April 2019
CAPE CANAVERAL, FL- For the first time ever we have heard the seismic sounds from
inside the alien Red Planet and they come in the form of the likely detection of what’s being called a ‘marsquake’ by NASA’s new InSight lander.
These signals are very exciting and a major discovery as they amount to the first
seismic detections beyond the Earth and Moon system.
“NASA’s Mars InSight
lander has measured and recorded for the first time ever a likely “marsquake” –
NASA said in a statement released April 23.
The discovery made on April 6, 2019 or Sol 128 marks
the first proof that the Mars of today is still “seismically active.”
“We’ve been waiting months for a signal like
this,” said Philippe Lognonné, SEIS team lead at the Institut de Physique du
Globe de Paris (IPGP) in France, in the NASA statement.
“It’s so exciting to finally have proof that
Mars is still seismically active. We’re looking forward to sharing detailed
results once we’ve had a chance to analyze them.”
And it’s the first recorded martian “trembling” emanating
from inside the Red Planet and not above the surface.
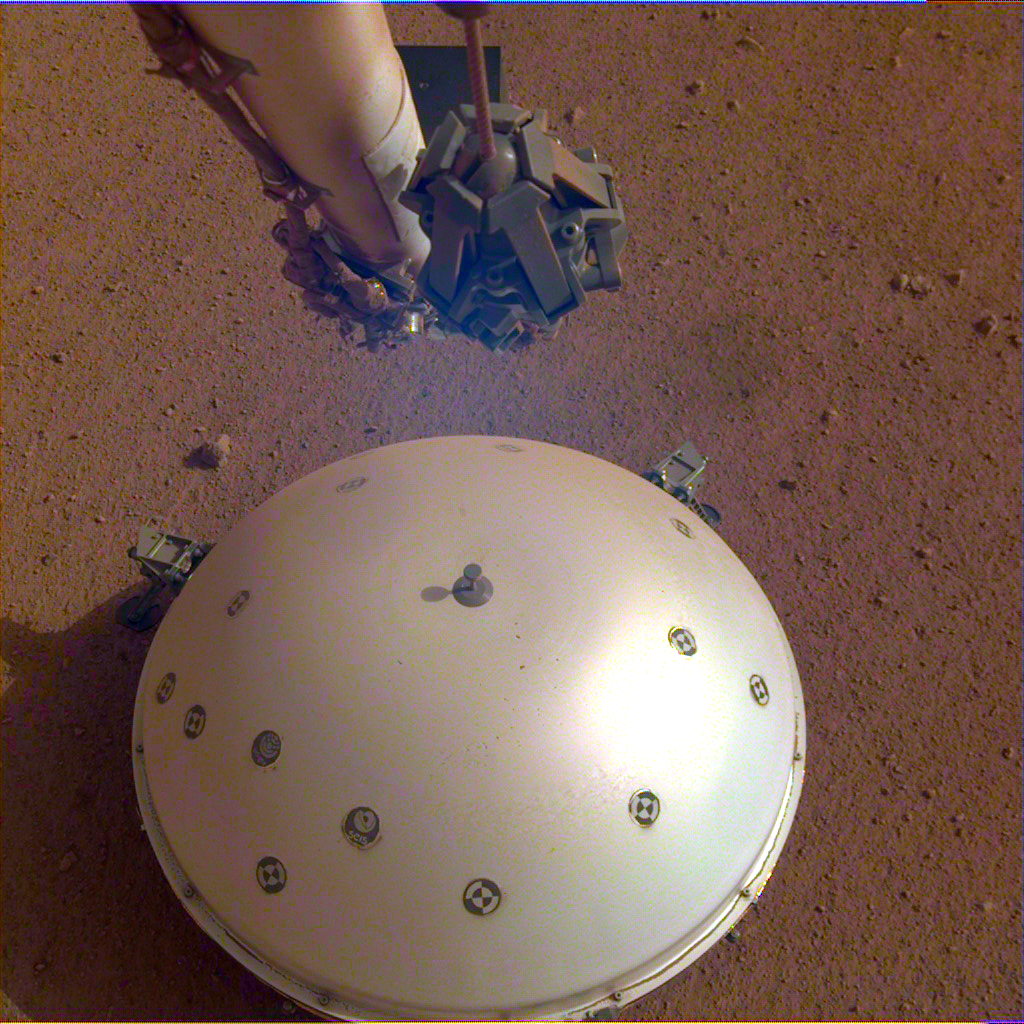
“The faint seismic signal, detected by the
lander’s Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS)
instrument, was recorded on April 6, the lander’s 128th Martian day, or sol.
This is the first recorded trembling that appears to have come from inside the
planet, as opposed to being caused by forces above the surface, such as wind.
Scientists still are examining the data to determine the exact cause of the
signal.”
Listen to the seismic signal recorded on April 6,
2019 and illustrated here:
Caption: This video and audio
illustrates a seismic event detected by NASA’s Mars InSight rover on April 6,
2019, the 128th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Three distinct kinds of
sounds can be heard, all of them detected as ground vibrations by the
spacecraft’s seismometer, called the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure
(SEIS): noise from Martian wind, the seismic event itself, and the spacecraft’s
robotic arm as it moves to take pictures.
Credits:
NASA/JPL-Caltech/CNES/IPGP/Imperial College London
is the first seismometer ever placed on the surface of another planet and will
be used to measure seismic waves caused by marsquakes, meteorite strikes and
other phenomena on Mars.
Here is further background on the Marsquake
detection from NASA’s Press release:
InSight’s first readings carry on the science
that began with NASA’s Apollo missions,” said InSight Principal Investigator
Bruce Banerdt of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena,
California. “We’ve been collecting background noise up until now, but this
first event officially kicks off a new field: Martian seismology!”
solid data on the Martian interior, which is one of InSight’s main objectives.
The Martian surface is extremely quiet, allowing SEIS, InSight’s specially
designed seismometer, to pick up faint rumbles. In contrast, Earth’s surface is
quivering constantly from seismic noise created by oceans and weather. An event
of this size in Southern California would be lost among dozens of tiny crackles
that occur every day.
its size and longer duration fit the profile of moonquakes detected on the
lunar surface during the Apollo missions,” said Lori Glaze, Planetary Science
Division director at NASA Headquarters.
seismometers that measured thousands of quakes while operating on the Moon
between 1969 and 1977, revealing seismic activity on the Moon. Different
materials can change the speed of seismic waves or reflect them, allowing
scientists to use these waves to learn about the interior of the Moon and model
its formation. NASA currently is planning to return astronauts to the Moon by
2024, laying the foundation that will eventually enable human exploration of
Mars.
planet’s surface on Dec. 19, 2018, will enable scientists to gather
similar data about Mars. By studying the deep interior of Mars, they hope to
learn how other rocky worlds, including Earth and the Moon, formed.
 |
|
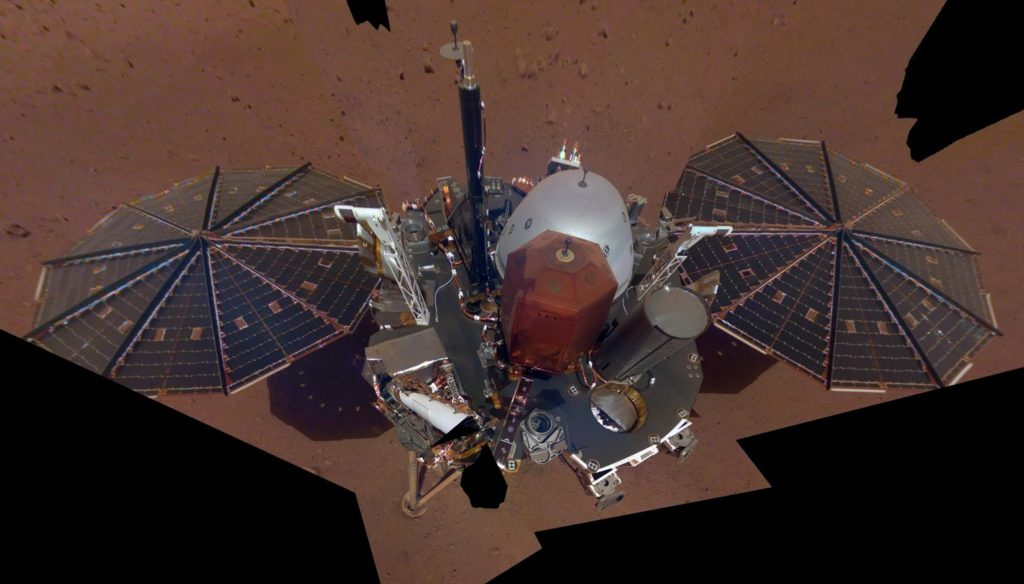
This is NASA InSight’s
first selfie on Mars. It displays the lander’s solar panels and deck. On top of the deck are its science instruments, weather sensor booms and UHF antenna. The selfie was taken on Dec. 6, 2018 (Sol 10). Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech |
Three other seismic signals occurred on March 14
(Sol 105), April 10 (Sol 132) and April 11 (Sol 133). Detected by SEIS’ more
sensitive Very Broad Band sensors, these signals were even smaller than the Sol
128 event and more ambiguous in origin. The team will continue to study these
events to try to determine their cause.
which occur on faults created by the motion of tectonic plates. Mars and the
Moon do not have tectonic plates, but they still experience quakes – in their
cases, caused by a continual process of cooling and contraction that creates
stress. This stress builds over time, until it is strong enough to break the
crust, causing a quake.
of engineering. On Earth, high-quality seismometers often are sealed in
underground vaults to isolate them from changes in temperature and weather.
InSight’s instrument has several ingenious insulating
barriers, including a cover built by JPL called the Wind and Thermal
Shield, to protect it from the planet’s extreme temperature changes and high
winds.
terms of its sensitivity. The instrument was provided for InSight by the French
space agency, Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), while these first
seismic events were identified by InSight’s Marsquake Service team, led by the
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology.
are eager to make many similar measurements with SEIS in the years to come,”
said Charles Yana, SEIS mission operations manager at CNES.
……
InSight soft landed on Mars on Nov 26,
2018, following a 7 month, 301 million mile (484 million km) interplanetary
journey from Earth. She has begun a 2-year mission to explore the Red Planet’s
mysterious deep interior.
in an international science mission. Loaded aboard are the two primary science
instruments provided by European partners from France and Germany: The SEIS
seismometer and HP3 heat flow
measuring instrument.
SEIS seismometer instrument is equipped with a trio of incredibly precise
seismometers to detect marsquakes and was provided by the Centre National
d’Études Spatiales (CNES) – the French national space agency equivalent to
NASA.
other instrument measuring heat flow from the Martian interior is provided by
the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and is named Heat Flow and Physical
Properties Package (HP3).
onsite coverage of NASA, SpaceX, ULA, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman
and more space and mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center, Cape
Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida and Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia.
Planetary science and human spaceflight news: www.kenkremer.com –www.spaceupclose.com – twitter @ken_kremer
– email: ken at kenkremer.com
KSC area, active in outreach and interviewed regularly on TV and radio about
space topics.
Ken’s photos are for sale and he is available for lectures and outreach events
Falcon 9/CRS-17 launch to ISS, Falcon 9 Beresheet launch, USAF GPS 3-01, NASA missions, ULA Atlas &
Delta launches, SpySats and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events at Quality Inn Kennedy Space Center, Titusville,
FL, evenings:
28-30: “SpaceX Falcon 9 Demo-1
and Beresheet
launch, Dragon CRS-17 resupply
launch to ISS, SpaceX Falcon Heavy & Falcon 9 launches, upcoming SpaceX
Falcon 9 ULA, NRO & USAF Spysats, SLS, Orion, Boeing and SpaceX Commercial
crew capsules, OSIRIS-Rex, Juno at Jupiter, InSight Mars lander, Curiosity and
Opportunity explore Mars, NH at Pluto, Ultima Thule, Kuiper Belt and more,”
Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings. Photos for sale